Understanding Bridge Fees and Transaction Times for Crypto Transfers
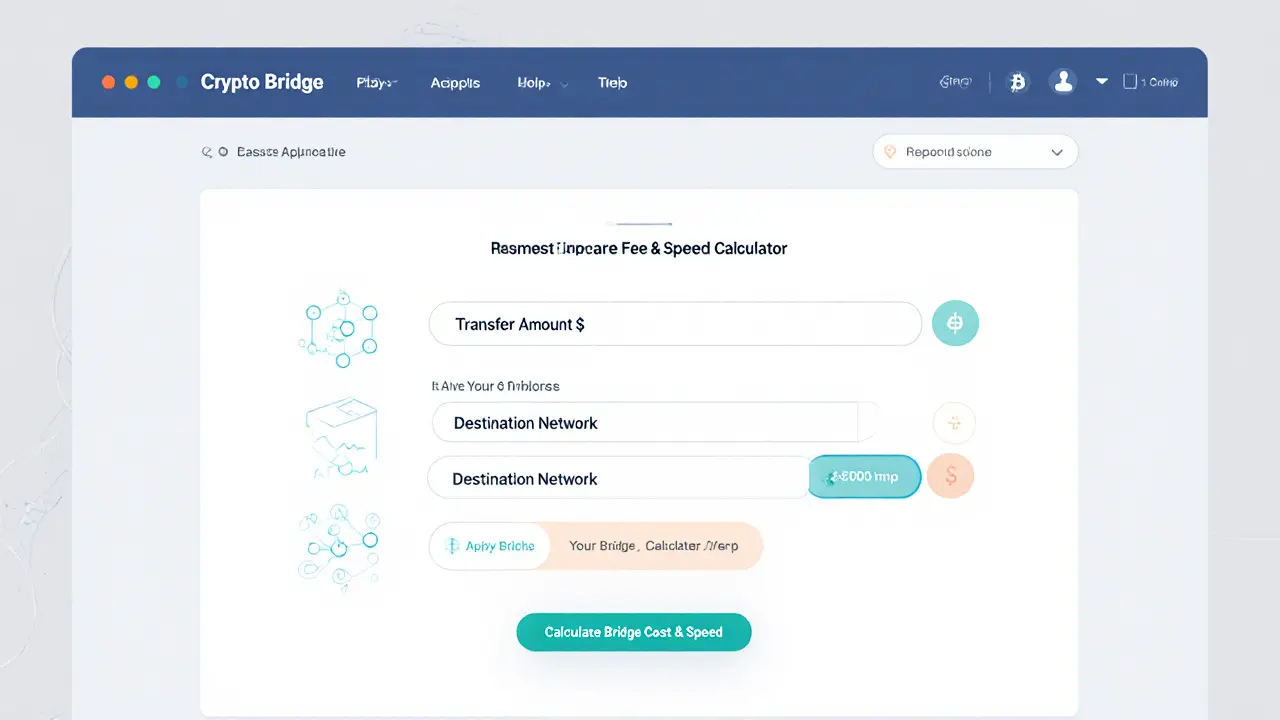
Crypto Bridge Fee & Speed Calculator
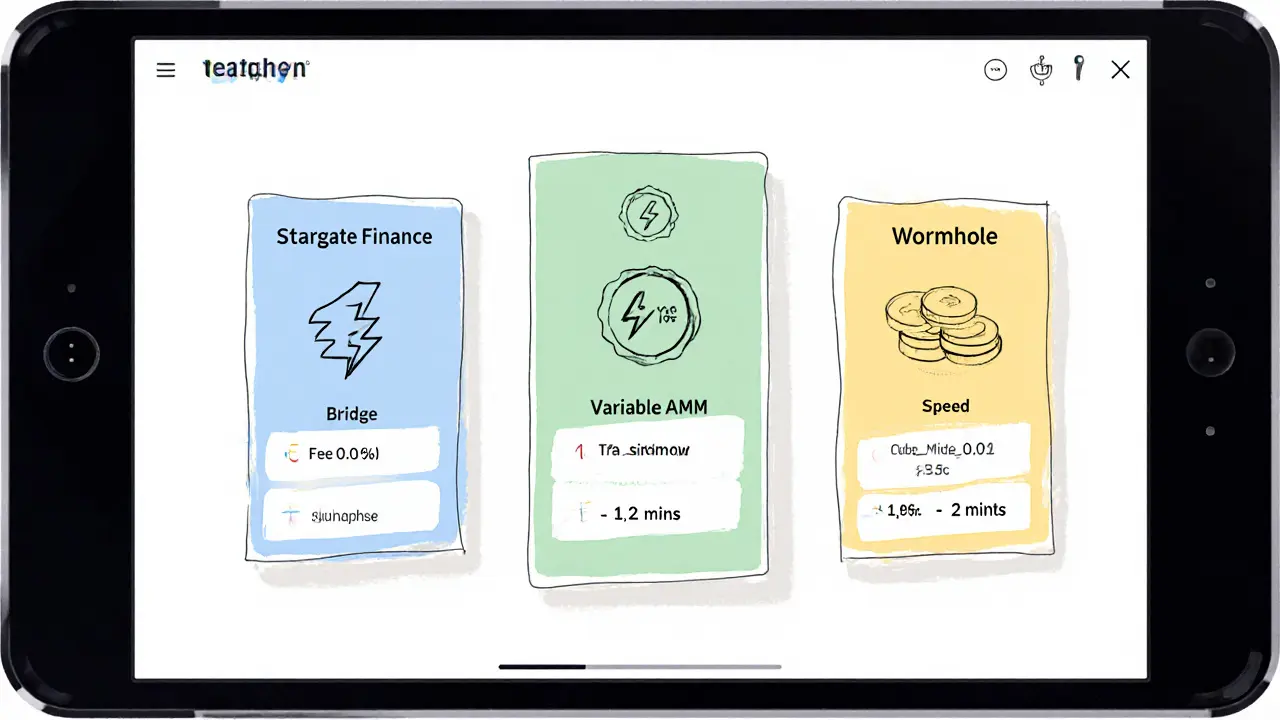
Popular Bridges Comparison
Stargate Finance
Flat 0.06%
Sub-second
Fast, fixed fee bridge
Synapse
Variable AMM
1-5 mins
Dynamic fee model
Wormhole
Sub-$0.01
1-2 mins
Low-cost for small transfers
When you move tokens between blockchains, two things dominate the decision: how much you pay and how fast it arrives. These are the bridge fees and the transaction times that vary wildly across providers, networks, and bridge designs. Below you’ll find a practical guide to decode the cost structures, speed expectations, and the trade‑offs you’ll face on today’s leading bridges.
What a Bridge Actually Does
Cryptocurrency bridge is a protocol that locks assets on one chain and issues equivalent tokens on another, enabling cross‑chain movement. The process involves a locking contract on the source chain, validator confirmation, and a minting (or releasing) contract on the destination chain. Depending on the architecture, the bridge may be centralized, trustless, unidirectional, or bidirectional, each influencing cost and speed.
Fee Models: Fixed vs. Variable
Bridge operators charge for the work of moving assets. Two dominant pricing mechanisms dominate the market.
- Fixed‑fee models apply a flat percentage or a static amount per transfer. For example, Stargate Finance charges about 0.06% per transaction, regardless of the amount.
- Variable AMM (Automated Market Maker) models adjust fees based on liquidity depth and slippage risk. Bridges like Synapse or Symbiosis modulate fees in real‑time, sometimes saving up to 80% compared with flat‑fee rivals.
Fees typically range from 0.05% to 0.3% of the transferred value, but ultra‑low options exist. Wormhole offers sub‑$0.01 flat fees for many routes, making it attractive for small transfers.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Bridges
Centralized bridges-think Binance Bridge operated by the Binance exchange, offering fast, low‑cost swaps under a single trusted entity-generally deliver quicker finality and cheaper fees because they bypass extensive on‑chain validation. The trade‑off is that users must trust the operator not to mishandle funds.
Decentralized, trustless bridges rely completely on smart contracts and validator signatures. While they give users full custody, the extra computation and multi‑signature verification raise both fees and latency. Examples include Stargate Finance and Synapse. Their security stems from the underlying blockchains (Ethereum, BSC, etc.) rather than a central authority.
Typical Processing Times Across Popular Networks
The speed you experience depends on two layers: the source/destination blockchain's block time and the bridge’s own confirmation logic.
| Bridge | Fee Model | Avg. Fee | Avg. Transfer Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stargate Finance | Flat 0.06% | 0.06% (≈ $0.15 on $250 transfer) | Sub‑second finality, <2seconds total |
| Wormhole | Flat (under $0.01) | ≈ $0.008 per transfer | ~5‑10seconds (depends on source chain) |
| Synapse | Variable AMM | 0.08%‑0.25% (liquidity dependent) | 2‑5minutes (routing & slippage checks) |
| Binance Bridge | Flat 0.05% (centralized) | 0.05% (≈ $0.13 on $250 transfer) | ~3‑6seconds (central ledger sync) |
| Symbiosis | Variable AMM | 0.07%‑0.22% | 1‑3minutes (aggregator routing) |
Ethereum‑based bridges tend to be slower during network congestion because each on‑chain step requires gas. Even with a 5‑second block time, finality can stretch to ~13minutes when the network is busy. By contrast, Binance Smart Chain (BSC) offers 3‑second block times and typically reaches finality within 5minutes, making BSC‑linked bridges faster for larger volumes.
How Transaction Size and Network Congestion Influence Fees
Larger transfers-both in value and data payload-consume more gas, especially on complex smart contracts. When you send a simple ERC‑20 token, the gas cost might be ~50,000 units, but a multi‑step bridge that mints, locks, and verifies can push consumption beyond 200,000 units. During peak periods on Ethereum, the same operation can jump from $5 to $30 in gas, inflating the effective bridge fee.
To mitigate spikes, many wallets let you preview the estimated network fee before confirming. The fee you set directly impacts speed: a higher gas price speeds up confirmation, while a lower price can add minutes or even hours, depending on the chain’s mempool.
Choosing the Right Bridge for Your Use Case
Think about three practical dimensions: cost sensitivity, speed urgency, and trust tolerance.
- Micro‑transactions (<$50): Wormhole or Binance Bridge shine because their flat sub‑$0.01 fees dwarf percentage‑based costs.
- Medium‑size swaps ($100‑$5,000) where price impact matters: Variable‑AMM bridges like Synapse or Symbiosis often find a cheaper route by tapping deep liquidity pools.
- Large, time‑critical moves (>$10,000+): Stargate Finance’s sub‑second finality or a centralized solution such as Binance Bridge can guarantee the funds land quickly, albeit with a modest fee.
Remember that centralized bridges require you to trust the operator’s custodial practices. If regulatory compliance or custody risk is a concern, stick with trustless options-even if they cost a few percentage points more.
Security Considerations Specific to Bridges
Bridges have become high‑profile attack vectors. A successful exploit can steal millions because the bridge holds locked assets on one chain and minted equivalents on another. Key security practices include:
- Check whether the bridge’s contracts have been audited by reputable firms (e.g., CertiK, QuantStamp).
- Prefer bridges that use multi‑signature validator sets rather than a single admin key.
- Watch for community reports of “bridge hacks” - the past three years saw several exploits on untested AMM bridges.
- Use a hardware wallet when interacting with trustless bridges to keep private keys offline.
Even with robust contracts, user error-like sending to the wrong network or selecting the wrong token version-can lead to loss. Always double‑check the destination chain and token symbol in the UI before confirming.
Future Trends Shaping Bridge Fees and Speed
Developers are actively working on three fronts that could reshape the landscape by 2026.
- Layer‑2 rollups (e.g., Arbitrum, Optimism) are being integrated into bridge routes, promising sub‑second finality on Ethereum‑compatible chains.
- Cross‑chain messaging standards like Interchain Messaging Service (IMS) aim to replace custom validators with a universal proof system, potentially lowering overhead.
- Liquidity aggregation engines are getting smarter, using AI to predict slippage and automatically split large transfers across multiple routes, shaving both fees and time.
Keep an eye on the roadmap pages of Stargate, Synapse, and Symbiosis; many promise “single‑slot finality”-a concept that could bring Ethereum’s 13‑minute finality down to under a minute.
Quick Checklist Before You Bridge
- Identify source and destination chains.
- Pick a bridge that supports both networks (centralized or trustless).
- Check the current fee model (fixed vs. variable) and estimate cost.
- Verify network congestion; adjust gas price if speed matters.
- Confirm the bridge’s audit status and validator composition.
- Use a hardware wallet for large, trustless transfers.
- Record the transaction hash on both chains for future reference.

Frequently Asked Questions
Why do some bridges charge a flat fee while others use a variable fee?
Flat fees simplify pricing for users-what you see is what you pay. Variable fees, often powered by AMM algorithms, reflect real‑time liquidity depth and slippage risk, allowing the bridge to pass savings when markets are deep.
Is a centralized bridge safer than a decentralized one?
Safety is a trade‑off. Centralized bridges are faster and cheaper but require trust in the operator’s custodial controls. Decentralized bridges keep you in full control of your keys, but higher fees and longer confirmation times reflect the extra validation steps needed.
How can I reduce the chance of paying high gas fees on Ethereum?
Monitor the network’s gas price using tools like Etherscan Gas Tracker, schedule transfers during off‑peak hours, and set a custom gas price slightly above the median to balance cost and speed.
Can I bridge assets without paying any fees?
No. Even “zero‑fee” bridges still require network gas on the source chain, which users must cover. Some platforms subsidize the fee with their native token, but the underlying transaction cost remains.
What happens if a bridge transaction fails halfway?
A well‑designed bridge rolls back the first leg (the lock on the source chain) if the second leg cannot complete, returning the assets to the original address. However, users may lose the gas spent on the failed attempt.

Megan King
July 18, 2025 AT 06:08Hey, great start on breaking down those bridge fees! Remember, when you’re moving larger sums, the flat‑fee options like Stargate can save you a lot of extra cost. Keep testing the calculator with different amounts to see the sweet spot for each network.
Rachel Kasdin
July 21, 2025 AT 17:33America's blockchain future is gonna dominate, no doubt.
Nilesh Parghi
July 25, 2025 AT 07:41When you stare at the numbers behind bridge fees, you’re really peeking at the economics of trust. Each transaction is a tiny contract between decentralized actors, and the cost reflects the risk they shoulder. Variable AMM models, like Synapse, embed market‑making incentives into the fee itself. Fixed‑rate bridges, on the other hand, hide that market signal behind simplicity. In the end, your choice says something about how you value predictability versus price efficiency.
Raphael Tomasetti
July 29, 2025 AT 00:38TL;DR – if you need speed, go sub‑second with Stargate; if you’re okay with a minute or two, Wormhole is cheap. TVL and LP depth matter when you pick variable models.
Jenny Simpson
August 1, 2025 AT 20:23Oh, the drama of choosing a bridge! One moment you’re basking in the glow of a sub‑second transfer, the next you’re haunted by a hidden variable fee. It’s like watching a thriller where the villain is a hidden gas cost. Yet, the suspense makes the crypto world oddly romantic.
Rahul Dixit
August 5, 2025 AT 18:56Look, the system is rigged by the elites who hide fees behind sweet UI. They want you to think it’s free while they skim off the top. Wake up, or you’ll keep paying the hidden tax.
Enya Van der most
August 9, 2025 AT 20:18Let’s get moving! Test the calculator, see the numbers dance, and pick the bridge that makes your wallet smile. You’ve got this – every click brings you closer to mastering the crypto flow.
karyn brown
August 14, 2025 AT 00:28Nice work on the UI! 😎💥 The fee badges are super clear, and the hover effect makes it feel premium. Keep polishing – maybe add a tooltip for AMM versus flat fees. 🌟
Sabrina Qureshi
August 18, 2025 AT 07:26Wow!!! This calculator is sooo helpful!!! I love seeing the sub‑second speeds!! The design is sleek!! Can't wait to try it with bigger amounts!!!!!
Michael Ross
August 22, 2025 AT 17:13Appreciate the clear layout. The fee breakdown is concise and useful.
Deepak Chauhan
August 27, 2025 AT 05:48Esteemed reader, permit me to observe that the fee structures are, in essence, reflective of macro‑economic forces. Yet, one must also consider the opportunistic nature of certain bridges. In practice, nuance reigns supreme, dear participant. 😐
Aman Wasade
August 31, 2025 AT 21:11Oh yeah, because we all love waiting a solid minute for a $0.01 fee. Real cutting‑edge tech right there. 🙄
Andrew McDonald
September 5, 2025 AT 12:36Honestly, the UI feels a bit… pedestrian. One would expect a more avant‑garde presentation for such a sophisticated tool. 🤔
Adeoye Emmanuel
September 8, 2025 AT 10:03While the optimism in the post is palpable, let us pause to interrogate the underlying assumptions about "speed" and "cost" in cross‑chain transfers. The premise that sub‑second finality is universally superior disregards scenarios where security trumps latency, for instance, high‑value moves on Ethereum that demand multiple confirmations. Moreover, the flat‑fee model presented as inherently advantageous fails to account for the dynamic liquidity conditions that can render variable fees more economical during periods of market stress. One must also consider the hidden custodial risks introduced by certain bridges that centralize validation, thereby exposing users to geopolitical or regulatory interference – a factor often omitted in superficial calculators. It is imperative, therefore, to weigh not only the raw numbers but also the architectural trust models, the provenance of the bridge’s smart contracts, and the audit provenance. Only through such a holistic examination can a user truly discern the optimal pathway for their assets. In practice, I recommend layering a risk matrix alongside the fee calculator, assigning weight to dimensions such as contract audit status, validator decentralization, and historical uptime. By doing so, the decision-making process transitions from a mere arithmetic exercise to a comprehensive risk‑adjusted analysis. Ultimately, the goal is to empower users with both quantitative and qualitative insights, ensuring that the chosen bridge aligns with their individual risk tolerance and strategic objectives.
Raj Dixit
September 9, 2025 AT 06:08Look, if you’re not reading the fine print, you’re just a sucker feeding the bridge oligarchs. Keep it simple: flat fees win, period.